Flex your muscles
Posted on September 27, 2022 • 3 minutes • 632 words
Do you have, or are wanting to have a fitness wearable or fitness tracking app? Then I’m pretty sure you know why you have them or do you? What is the biology of fitness? Is exercise mandatory for fitness? Today, your curious explorer is going to explore fitness, its biology and how to achieve it.
Often diseases like diabetes, coronary artery disease, and other lifestyle diseases blame inactivity as a major precipitating factor for the disease onset. Physical inactivity leads to obesity, high blood pressure, and cholesterol content in the body which in turn leads the lifestyle diseases. To combat these diseases, WHO recommends moderate-intensity physical activity of 150-300 minutes a week. This would mean approximately 20-40 mins of moderate-intensity activity per day. If looked closely, inappropriate food intake is the major problem and appropriate activity is the solution.
The food intake is governed by a variety of small-molecule messengers like GLP-1, PYY3-36, CCK, Ghrelin, and Leptin. While PYY increases, Ghrelin decreases immediately after food intake. Such changes in these messengers’ levels control a human’s satiety. These small molecules perfectly orchestrate to induce hunger only when food is expected/needed by the body. It is, therefore, appropriate to have food intake in symphony with these messengers‑in simple sense, having a fixed time for food intake. Although discipline in schedule alone does not guarantee a good eating lifestyle, the type of food plays a major role too. Nutrigenomic scientists find how food affects your genomic content, and you after that. Trans fat and saturated fats are known to increase cholesterol, clog arteries, and increase the risk for heart diseases.
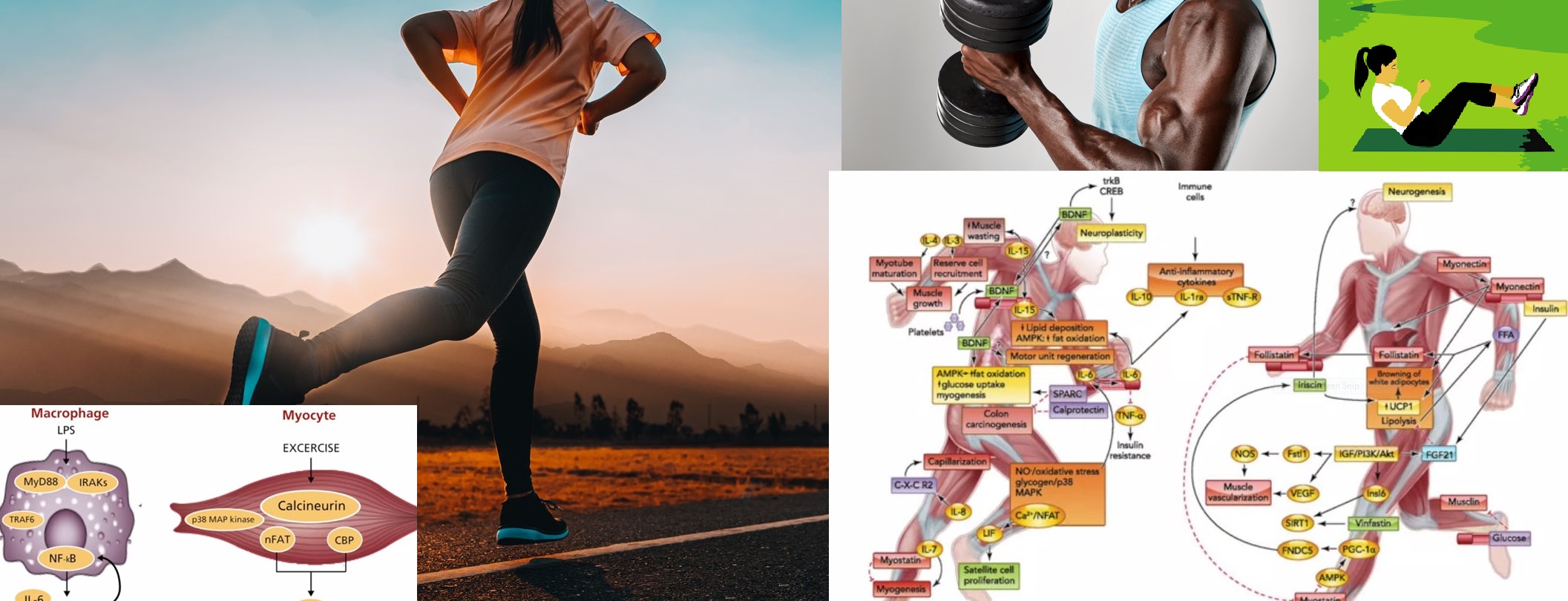
Exercise is the best way to combat the risk of these diseases. Muscles produce a meteorin-like myokine that aids in the browning of fat tissues and increases the usage of fat by the body. This reduces the risk of diabetes and cardiovascular diseases. Exercise not only helps you reduce fat in your body but makes muscles produce factors that strengthen themselves and other tissues of the body. Exercise stimulates follistatin that helps in the building of muscles and extracts crucial advantages from muscles. Muscles produce IL-6 which increases the immunity of the body. Muscles also significantly reduce anti-inflammatory activity in the body compared to a resting individual thereby increasing insulin sensitivity by regulating glucose transporter. It is believed that 7 days of inactivity could accelerate up to 9 years of ageing. Muscle-derived cytokines also aid in fat oxidation, increased glucose uptake, neurogenesis, increase neural plasticity, and increased capillarization.
The amount of energy expenditure is alone not enough for avoiding lifestyle diseases. The way in which physical activity is done is also essential for a healthy lifestyle. Although it extends the reach of this blog on what kinds of physical activities are essential, one might often wonder about the intensity of the activity done. While a few spend some quality and rigorous time in the gym, others have a lifestyle where they perform mild to moderate physical activity throughout the day. People who take public transport, having a job where they often walk are found to be more fit than those who do not walk or travel in their own vehicles. Although limited-intense physical activity and moderate-long activity both point to fitness, intense physical activities have benefits not to be found in normal activity. They accelerate angiogenesis, lipolysis of visceral fat, hepatic glucose production, and insulin production. An intense activity also produces endorphins that help you get addicted to exercise.
It is just an alarm and a commitment away from you to get started. If you work in an environment with lesser physical activity, it is wiser to spend at least an hour on your body when it spends the rest of the time on you. Arise, awake and stop not till the goal is reached.