ELISA
Posted on January 17, 2021 • 3 minutes • 553 words
When your hands are dealing with someone’s life, when a simple mistake you make could cause devastation, a slight variation in pressure could bring down hopes, when your hands are responsible for betterment of lives, and you are holding a micropipette, loading samples in a 96-well plate for Colorimetric assay, you definitely are a lab technician performing ELISA.
As are all my blog posts, this post is also written for noobs. I shall discuss the process of ELISA like the way you never heard. I shall take the practical approach, where you would do ELISA with me. All I need you to do is to assume that you are a lab technician, and you have received a serum sample from which you need to know if the patient is positive for ACA.
A doctor finds that this patient has excessive blood clots, and suspects the patient to have a condition called APS. It is known that patients with this condition would release Antibodies against a component called Cardiolipin (ACA). It is your turn to prove if the patient has ACA, and are the levels below the risk factor.
Looking practically, all you need to do is to follow all the instructions given on the ELISA ACA kit. We shall now look at what happens in every step.
##Dilute your sample
The serum is diluted with distilled water and a diluent present in the kit.
This reduces the content of ACA, and provides optimal conditions.
##Choose the required number of wells
The kit provides 96 wells (small containers with a maximum volume of 300 microlitres.)
The bottom of these wells are coated with Cardiolipin (a molecule to which ACA binds)
##Add the Diluted sample in the wells
Generally, the final volume entering the well would have only 1 microliter of the serum.
The ACA binds to the Cardiolipin coated on the bottom of the well.
You will have to wait for a while (~30 mins) for efficient and strong binding.
##Wash
You will discard all the unbound materials, and wash with water.
This also removes all loosely bound particles.
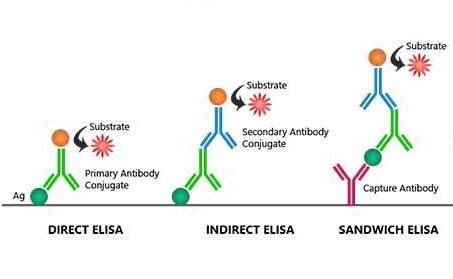
##Add the Enzyme conjugate
The kit provides secondary antibodies that bind to the ACA molecules.
These secondary antibodies have enzymes linked to them.
You will have to wait for a while for efficient binding before proceeding to next step.
##Wash
This will remove all the unbound and loosely bound material antibodies.
##Add Substrate
Various types of Enzyme-Substrate combinations are used by various kits.
##Incubate for appropriate time
The Enzyme reacts with substrate to give a coloured product.
The intensity of this colour can inform the amount of ACA present in the serum sample.
##Add Stop Solution
Generally, acid solution is added to stop the enzymatic reaction to take the readings.
##Take Readings Using the ELISA reader
The intensity of the colour is determined based on the Absorbance of light at specific wavelenght.
The computer now generates the amount of ACA present in the serum by comparing with a calibrator, and ensuring the positive and negative control.
This is how one would know quantitatively the levels of a specific biomarker in the serum. This result is then uploaded onto the computer, which is then viewed by the doctor to judge his prior analysis, and to take further decisions on the treatment and medications of the patient.